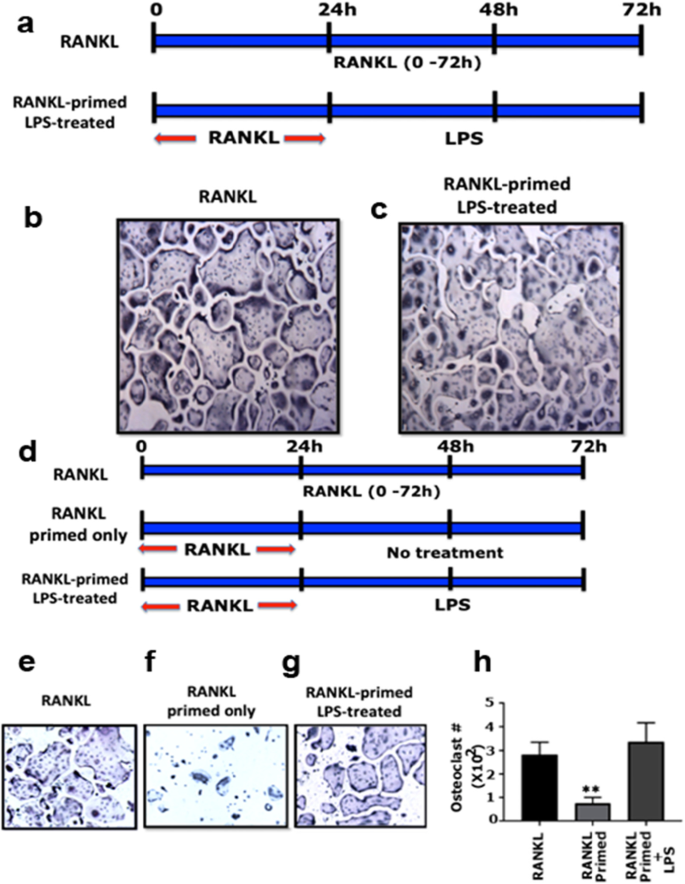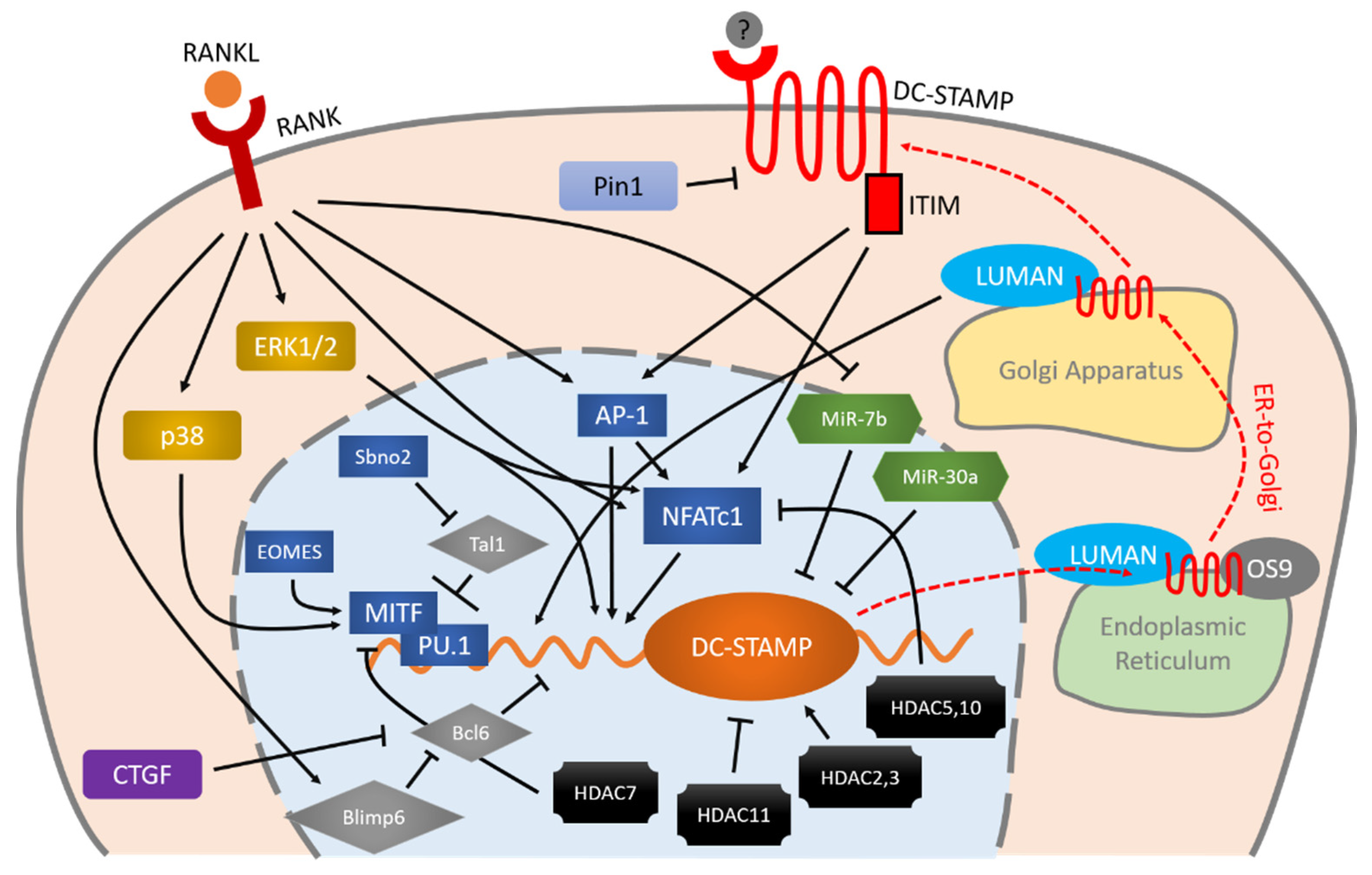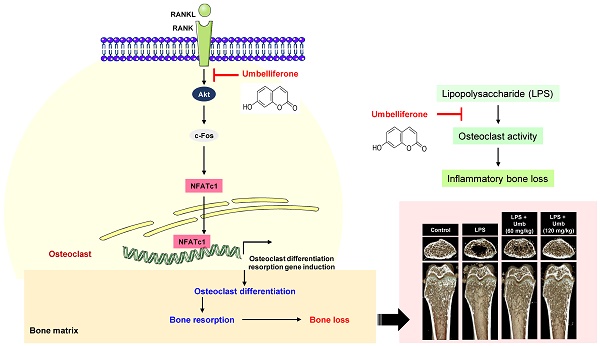
Umbelliferone Prevents Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Bone Loss and Suppresses RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Attenuating Akt-c-Fos-NFATc1 Signaling

Marine Drugs | Free Full-Text | Fucoidan Prevents RANKL-Stimulated Osteoclastogenesis and LPS-Induced Inflammatory Bone Loss via Regulation of Akt/GSK3β/PTEN/NFATc1 Signaling Pathway and Calcineurin Activity

Tablysin-15 inhibits osteoclastogenesis and LPS-induced bone loss via attenuating the integrin αvβ3 pathway - ScienceDirect
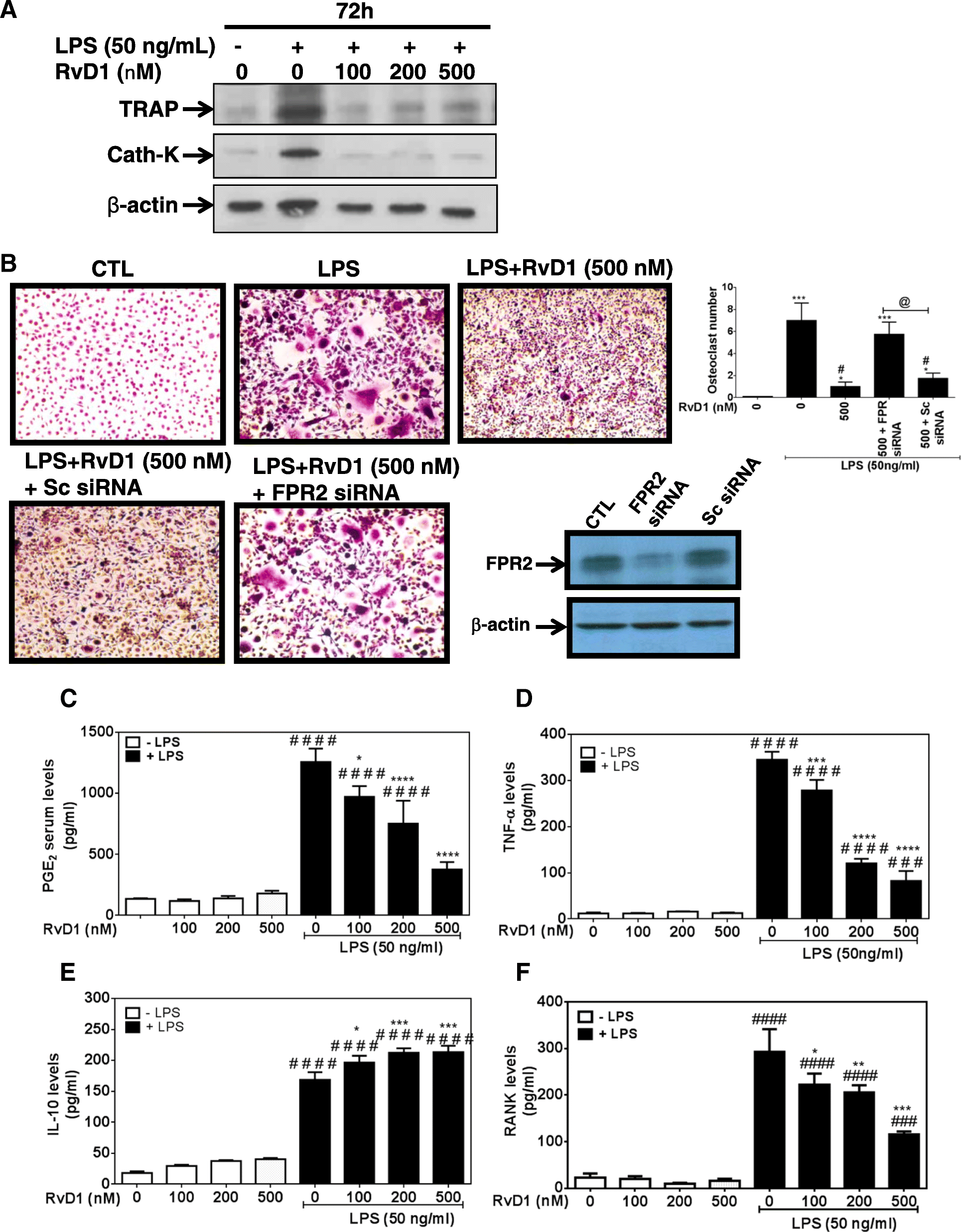
In vitro and in vivo assessment of the proresolutive and antiresorptive actions of resolvin D1: relevance to arthritis | Arthritis Research & Therapy | Full Text

Hesperetin suppresses RANKL‐induced osteoclastogenesis and ameliorates lipopolysaccharide‐induced bone loss - Liu - 2019 - Journal of Cellular Physiology - Wiley Online Library

Docosahexaenoic Acid Inhibits Inflammation-Induced Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption in vivo Through GPR120 by Inhibiting TNF-α Production in Macrophages and Directly Inhibiting Osteoclast Formation | Semantic Scholar
Loss of Protein Kinase C-δ Protects against LPS-Induced Osteolysis Owing to an Intrinsic Defect in Osteoclastic Bone Resorption | PLOS ONE

NLRP3 regulates alveolar bone loss in ligature‐induced periodontitis by promoting osteoclastic differentiation - Chen - 2021 - Cell Proliferation - Wiley Online Library

IJMS | Free Full-Text | NLRP3 Inflammasome Negatively Regulates RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis of Mouse Bone Marrow Macrophages but Positively Regulates It in the Presence of Lipopolysaccharides

CGRP inhibits LPS induced-osteoclast differentiation in vitro.: (a) Raw... | Download Scientific Diagram
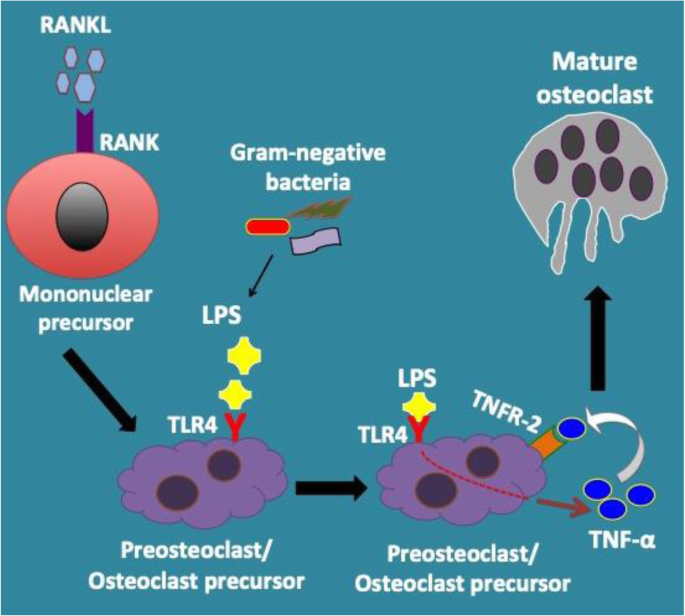
Lipopolysaccharide- TLR-4 Axis regulates Osteoclastogenesis independent of RANKL/RANK signaling | BMC Immunology | Full Text
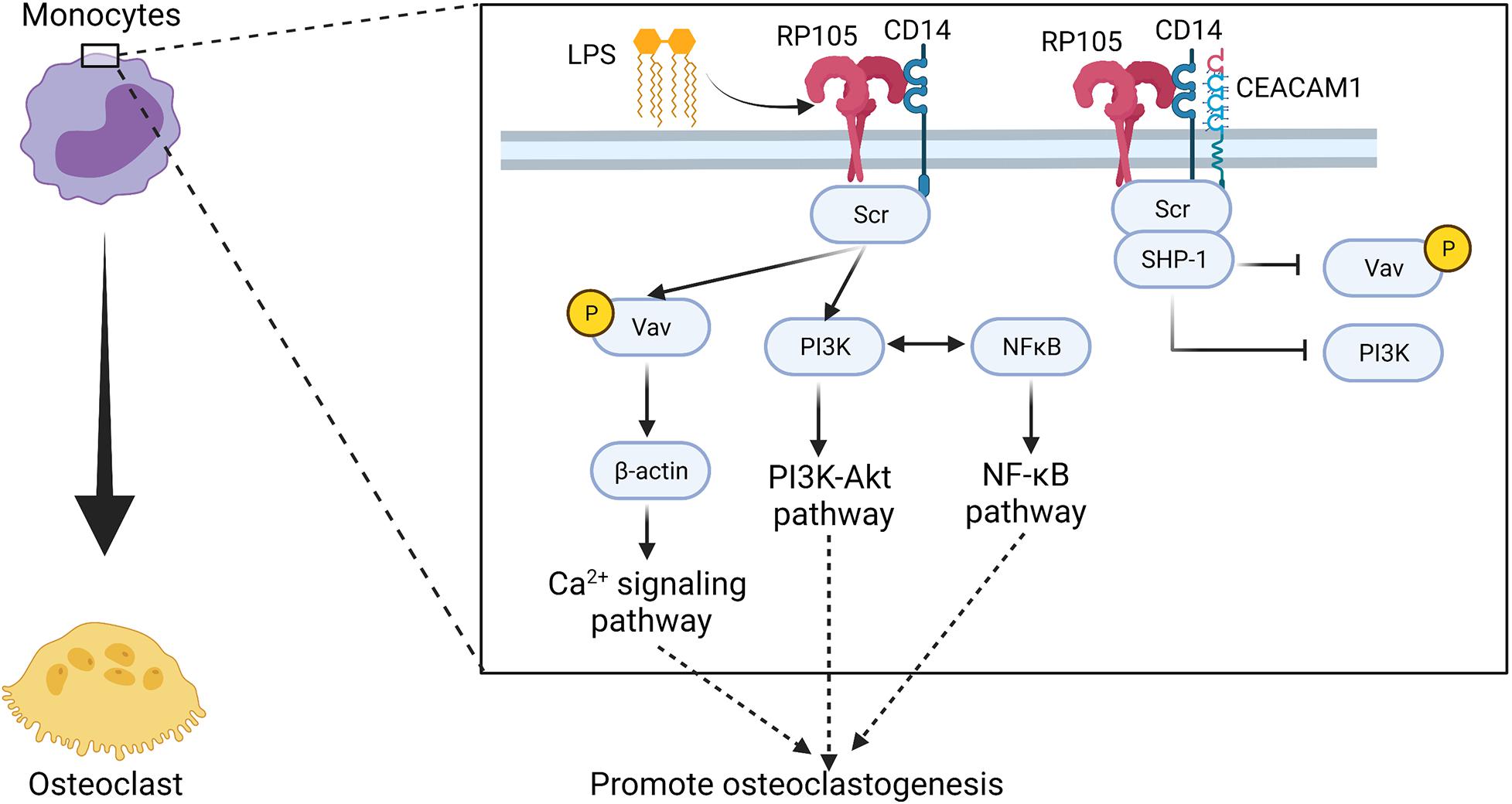
Frontiers | The Potential Role of RP105 in Regulation of Inflammation and Osteoclastogenesis During Inflammatory Diseases
Epothilone B prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory osteolysis through suppressing osteoclastogenesis via STAT3 signaling pathway - Figure f2 | Aging
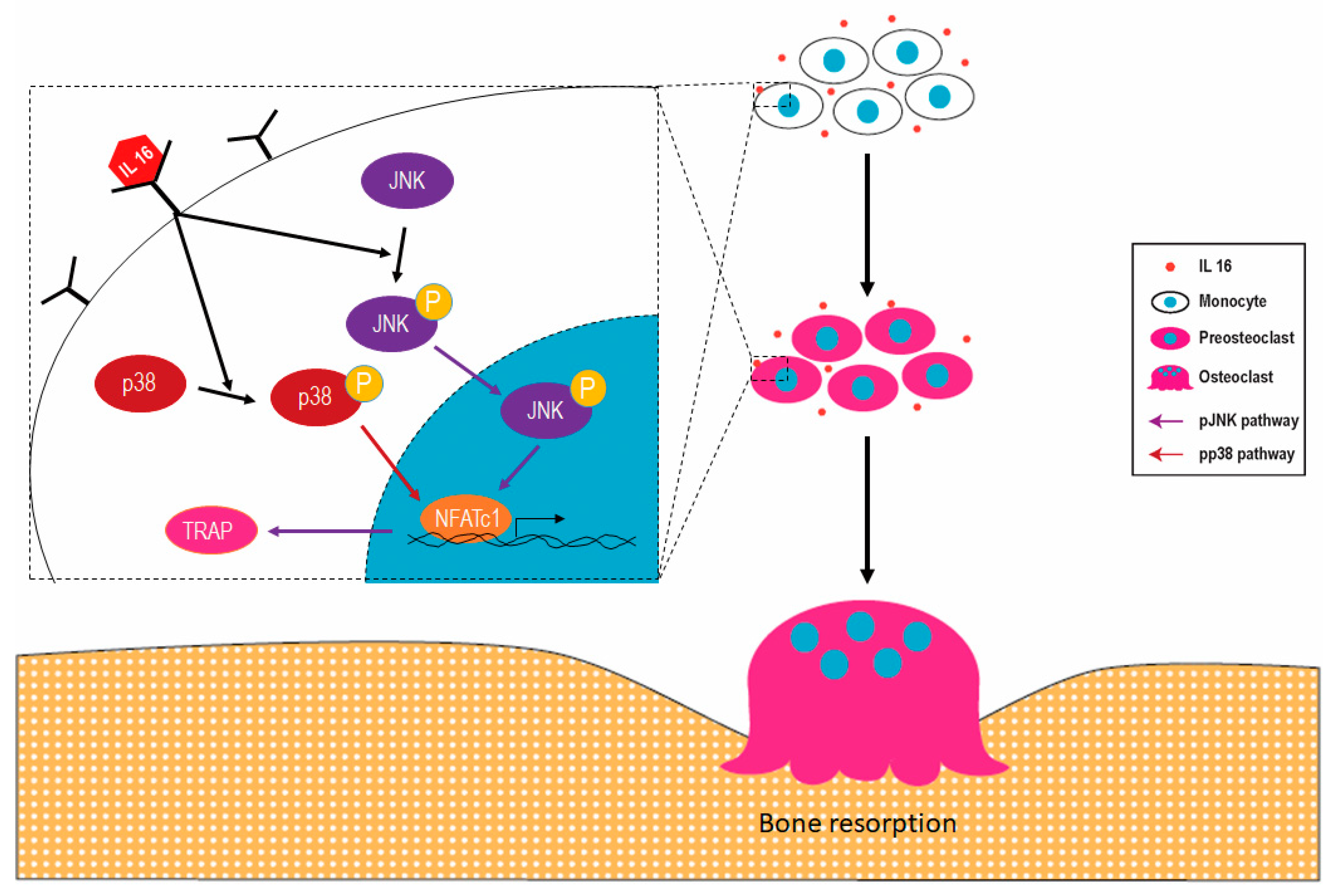
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Synovial Fluid Interleukin-16 Contributes to Osteoclast Activation and Bone Loss through the JNK/NFATc1 Signaling Cascade in Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection